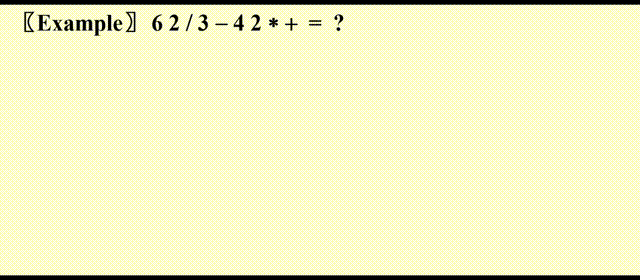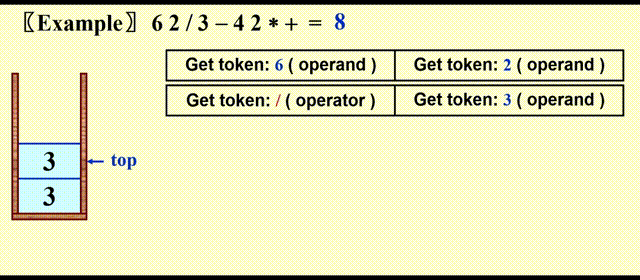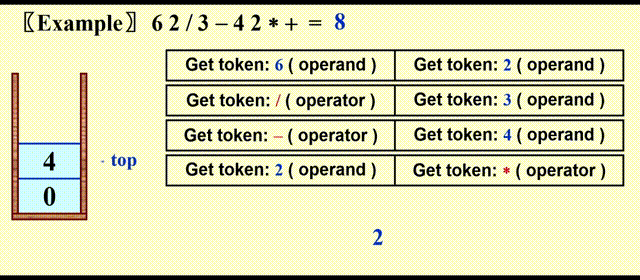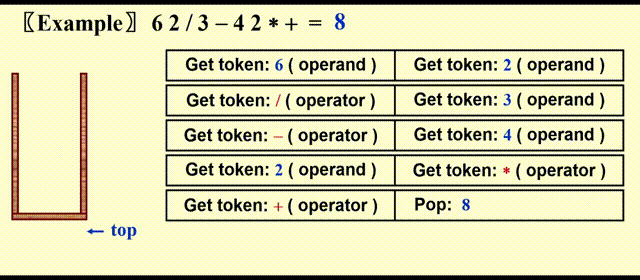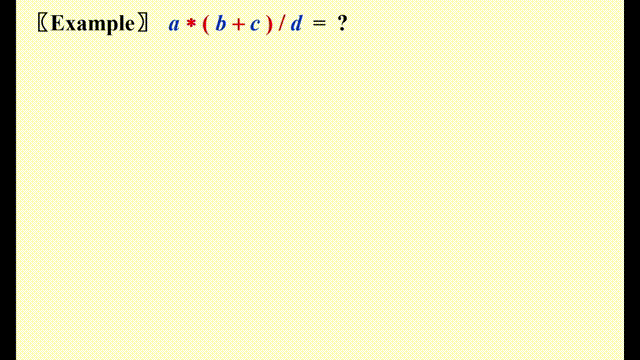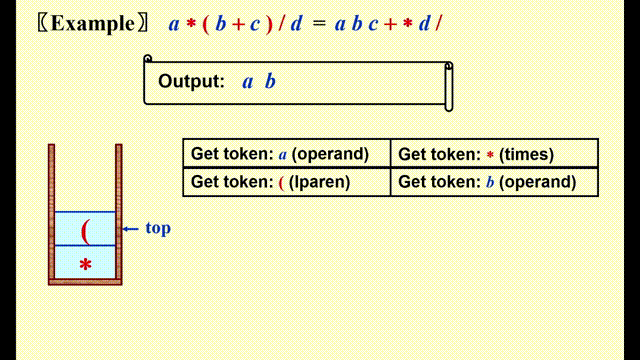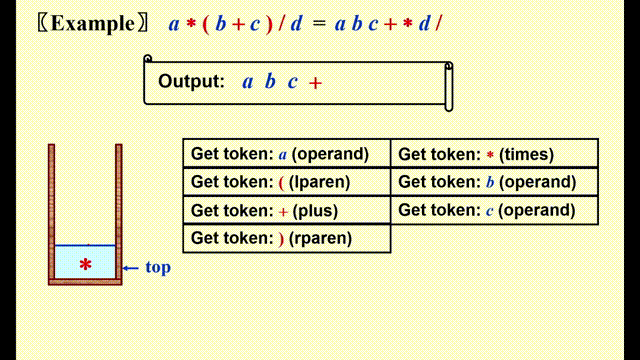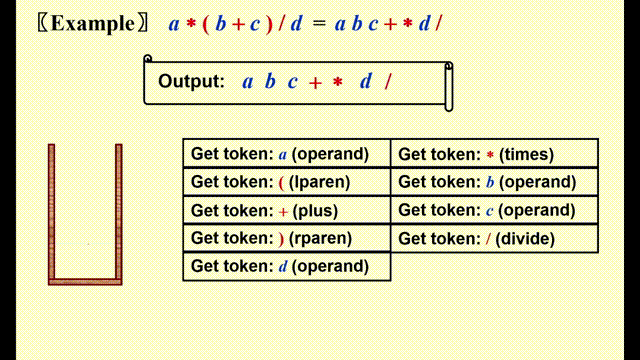Chap 3: Lists, Stacks, and Queues⚓︎
约 2201 个字 915 行代码 预计阅读时间 22 分钟
核心知识
- 列表
- 栈
- 操作:入栈、出栈 ...
- 应用:求解后缀,中缀转后缀 ...
- 队列
- 操作:入队、出队 ...
这 3 种 ADT 均有数组表示法和链表表示法
Abstract Data Type (ADT)⚓︎
数据类型 (data type) = { 对象 (objects)} \(\cup\) { 运算 (operations)}
抽象数据类型 (ADT)是将对象和运算的规范(就是我们定义的函数
The List ADT⚓︎
Simple Array Implementation of Lists⚓︎
- Objects: {\(item_0, item_1, \dots, item_{N - 1}\)}
-
Operations:
Finding_the_length:求链表长度 \(N\)Printing:打印列表所有元素Making_an_empty:建立空列表Finding:查找第 \(k\) 项,\(0 \le k < N\)Inserting:在第 \(k\) 项后插入新的项,\(k\) 的范围同上Deleting:删除一项Finding_next:查找下一个项Finding_previous:查找上一个项,用于删除列表首项
时间复杂度:
- 查找:\(O(1)\)
- 插入 & 删除:\(O(N)\)
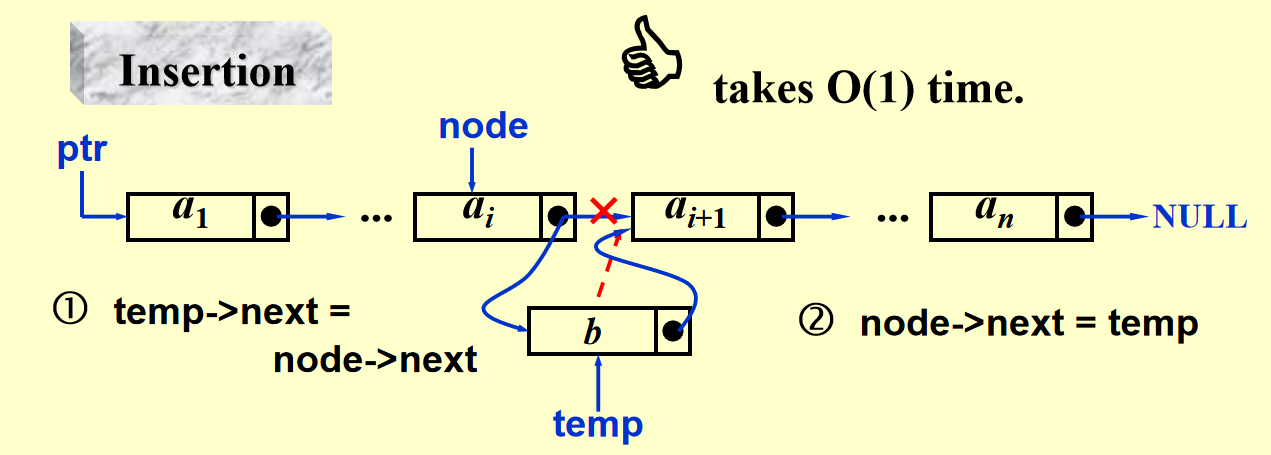
对于频繁进行插入和删除的列表,我们需要用到另一种实现形式——链表(linked list)
Linked Lists⚓︎
Note
- 链表相比数组占用空间更多(额外的指针域
) ,但它不要求空间连续 - 虽然查找时间慢(\(O(N)\)
) ,但插入和删除很快(\(O(1)\)) ,通过下面图示可以较为直观地感受到 - 最后一项的指针指向
NULL -
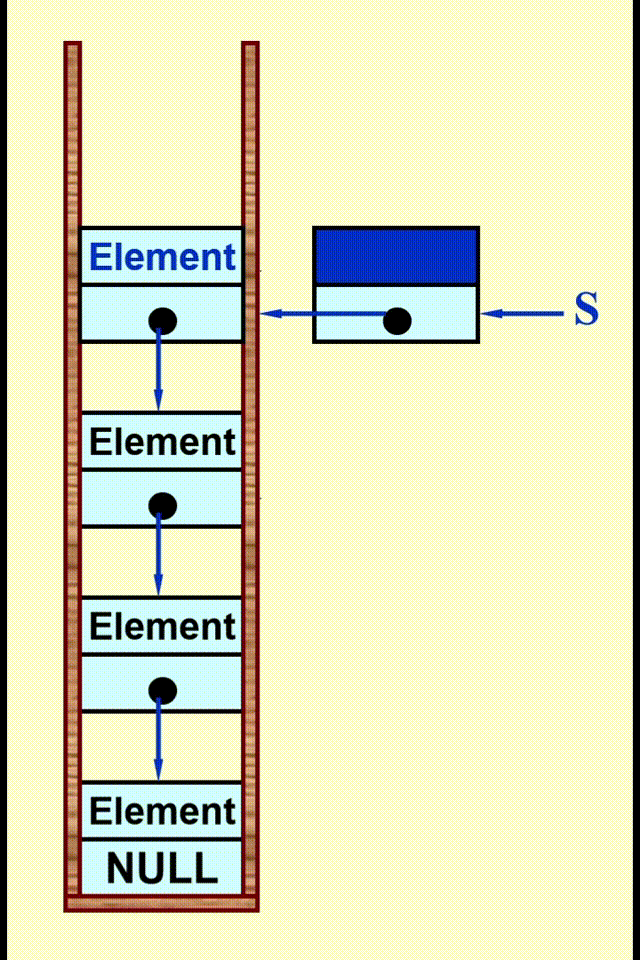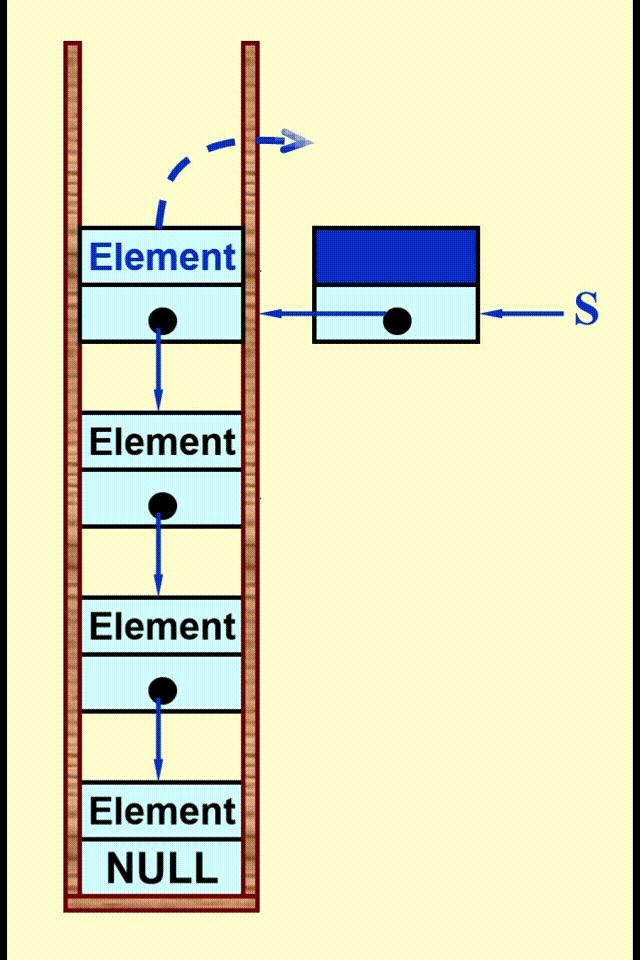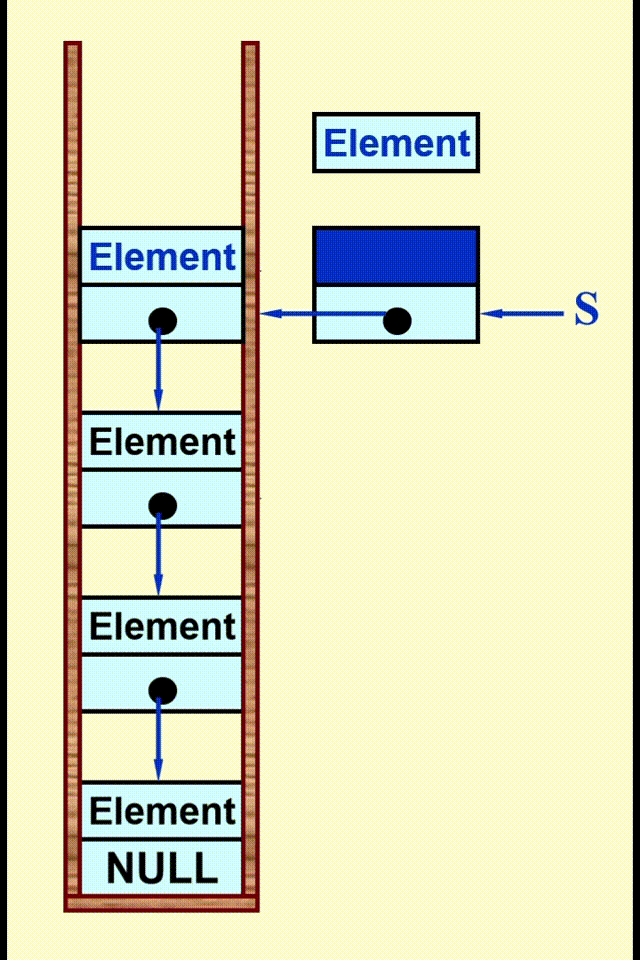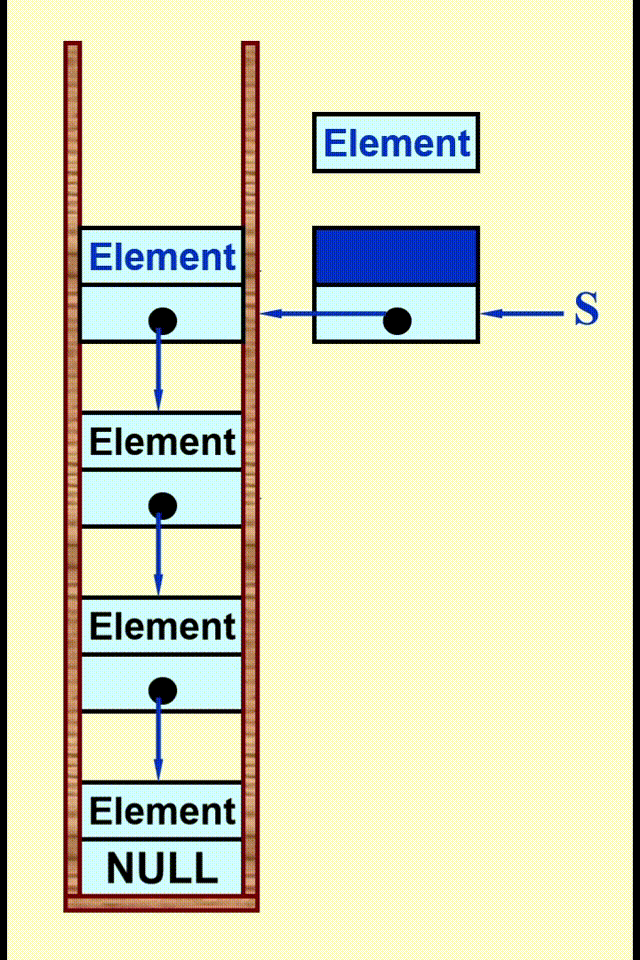
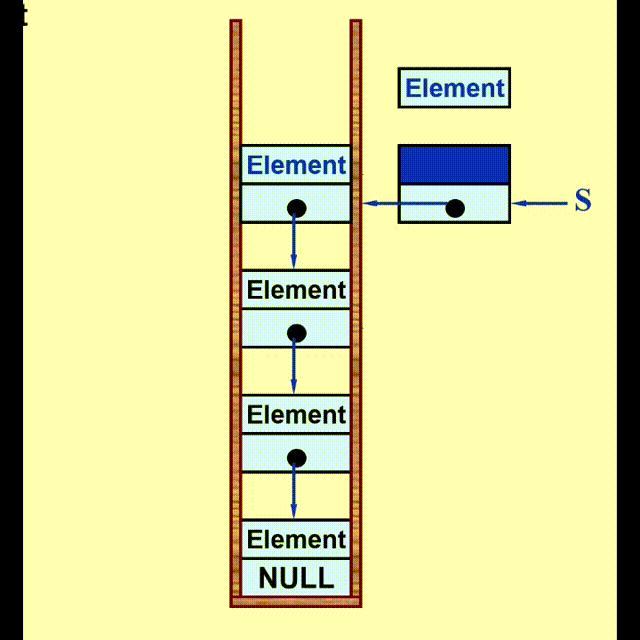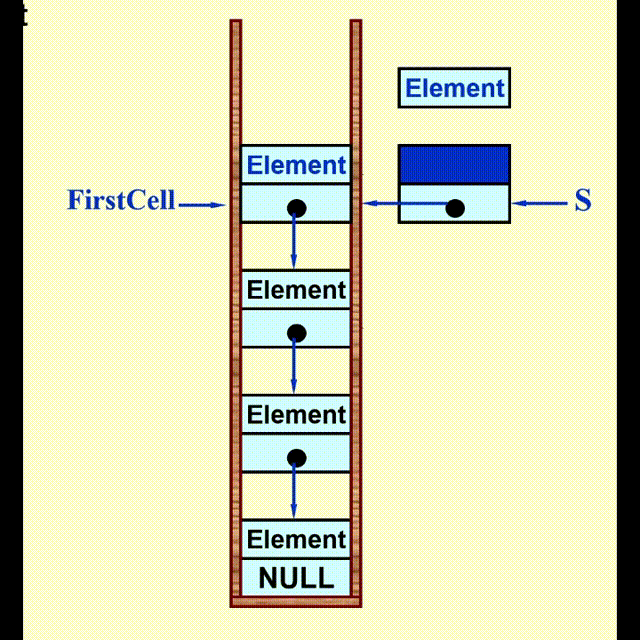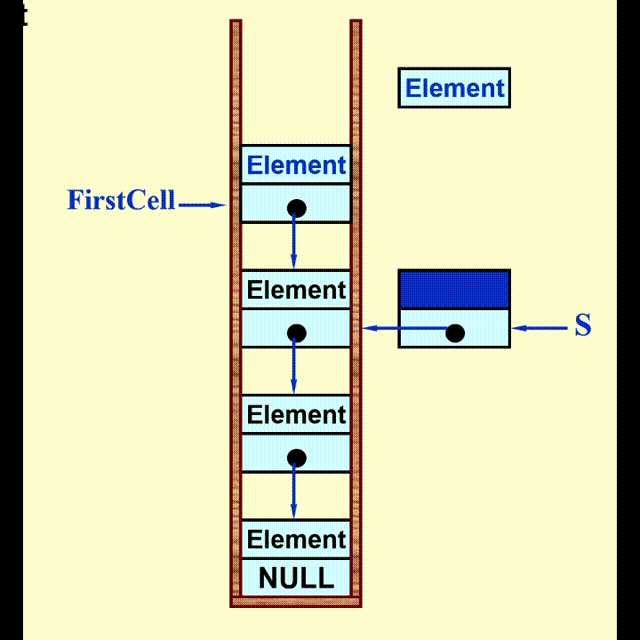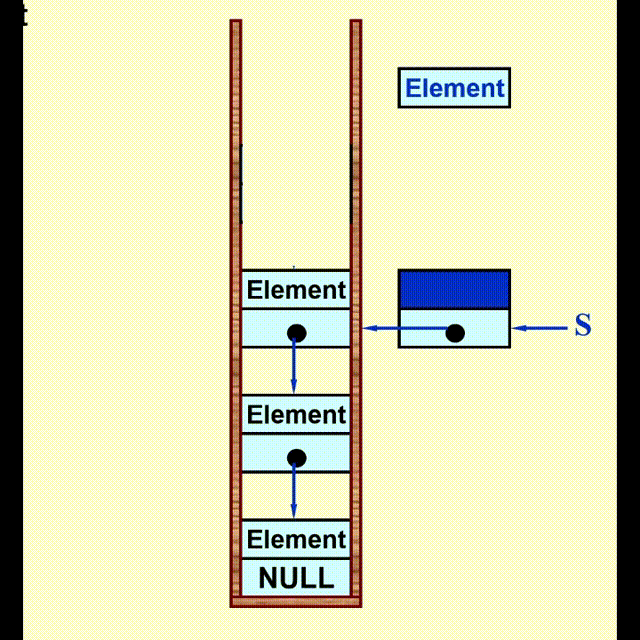
对于头指针,我们不将第一项作为头指针,而是采用一个虚拟节点 (dummy node)。这个节点数据域为空,指针指向列表中的第一项。这样做的好处有:
- 删除首项时无需使用
Finding_previous()了 - \(\dots\)
- 删除首项时无需使用
注:除非作特殊说明,FDS 中所有链表的实现默认将虚拟节点作为头指针
代码实现
// 链表的类型声明,一般放在 .h 文件中
#ifndef _List_H
struct Node;
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
typedef PtrToNode List;
typedef PtrToNode Position;
List MakeEmpty(List L);
int IsEmpty(List L);
int IsLast(Position P, List L);
Position Find(ElementType X, List L);
void Delete(ElementType X, List L, Position P);
Position FindPrevious(ElementType X, List L);
void Insert(ElementType X, List L, Position P);
void DeleteList(List L);
Position Header(List L);
Position First(List L);
Position Advance(Position P);
ElementType Retrieve(Position P);
#endif
// 链表的具体实现,一般放在.c文件中
// 节点
struct Node
{
ElementType Element;
Position Next;
};
// 检查链表是否为空
int IsEmpty(List L)
{
return L->Next == NULL;
}
// 检查节点 P 是否为最后一项
// 注意到链表 L 没有用上,放在这里是为了应付特殊情况的处理
int IsLast(Position P, List L)
{
return P->Next == NULL;
}
// 查找数据 X 在链表 L 中的位置
Position Find(ElementType X, List L)
{
Position P;
P = L->Next;
while (P != NULL && P->Element != X)
P = P->Next;
return P;
}
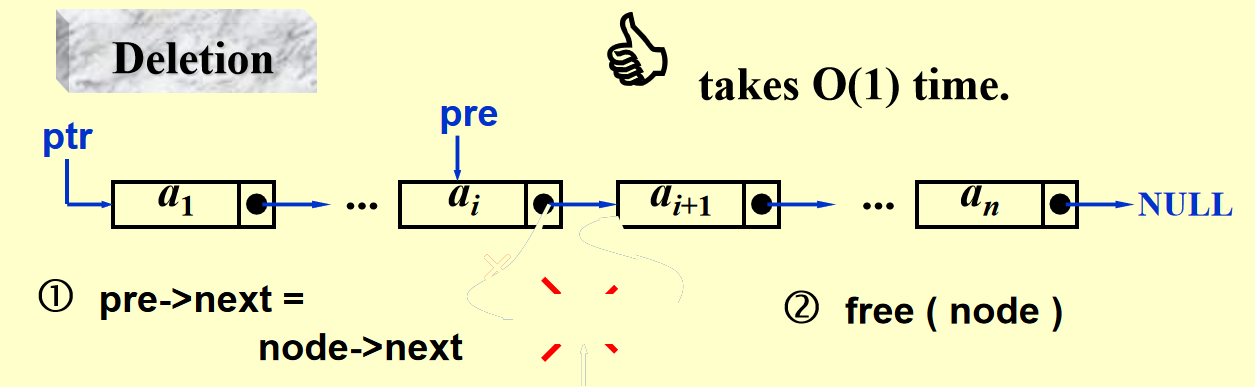
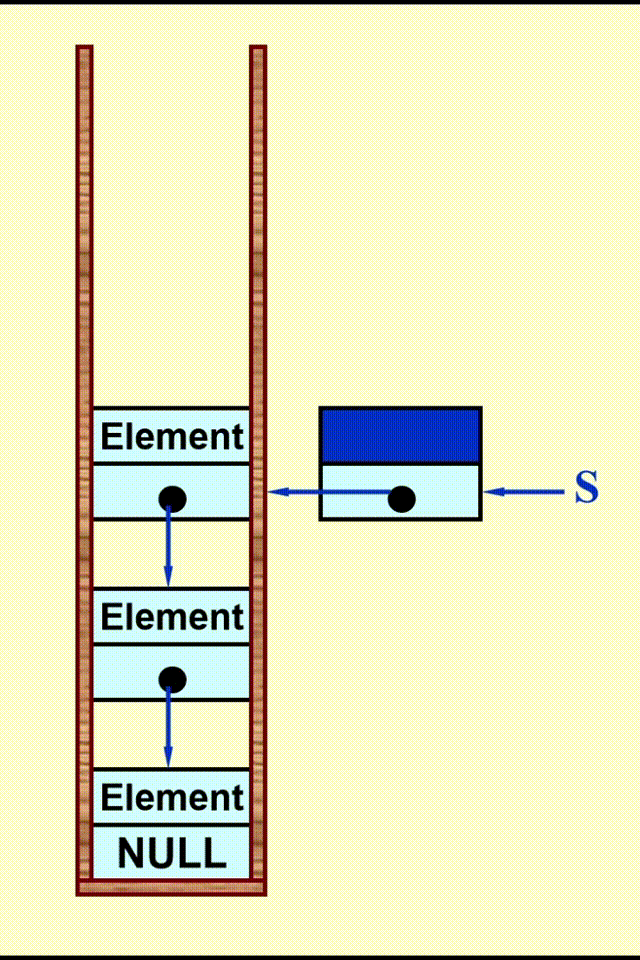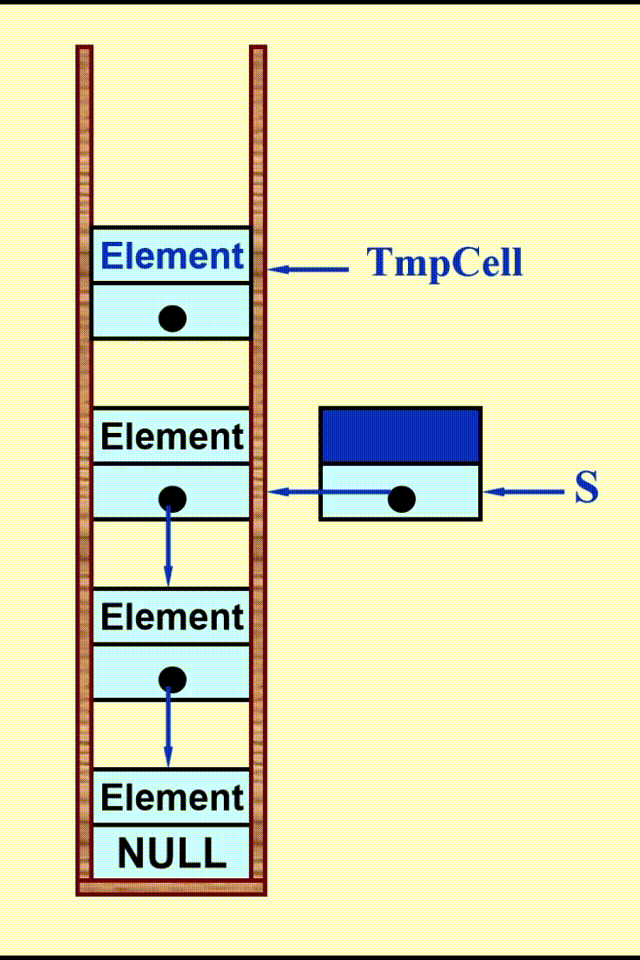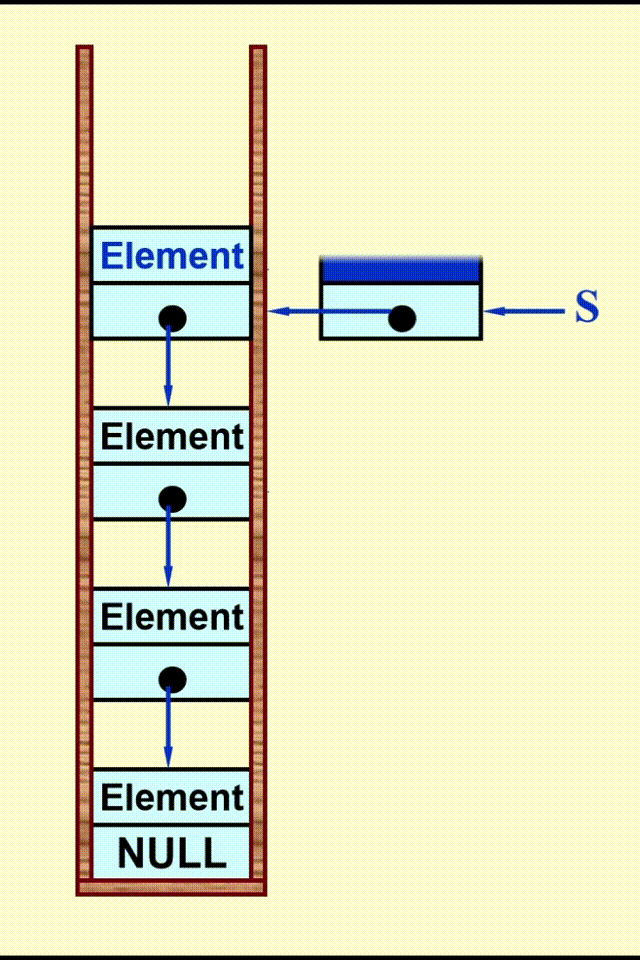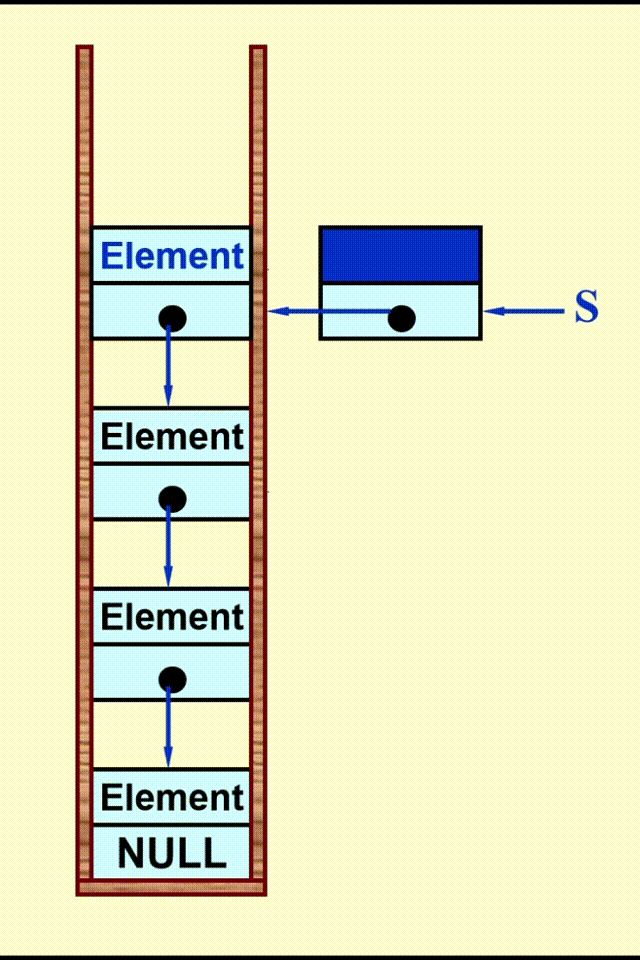
// 删除链表 L 中的数据 X
void Delete(ElementType X, List L)
{
Position P, TmpCell;
P = FindPrevious(X, L);
if (!IsLast(P, L))
{
TmpCell = P->Next;
P->Next = TmpCell->Next;
Free(TmpCell); // 删除节点时不要忘记释放内存!!!
}
}
// 查找前一项
Position FindPrevious(ElementType X, List L)
{
Position P;
P = L;
while (P->Next != NULL && P->Next->Element != X)
P = P->Next;
return P;
}
// 在位置 P 后插入新数据 X
void Insert(ElementType X, List L, Position P)
{
Position TmpCell;
TmpCell = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (TmpCell == NULL)
FatalError("Out of Space!!!"); // 这里用到处理错误信息的自定义函数
TmpCell->Element = X;
TmpCell->Next = P->Next;
P->Next = TmpCell;
}
Common Errors⚓︎
关于链表的常见错误
- 内存访问错误 (memory access violation) 或段错误 (segmentation violation):可能因为错误的初始化,或者引用不存在的指针(该指针已被
free()了) - 判断何时使用
malloc()- 如果想要创建一个之前未声明的指向结构的指针,需要用到
malloc() - 如果想要用指针遍历一遍链表,则无需使用
malloc()注意:
malloc()是给指针分配存储空间,而不是用于结构的
- 如果想要创建一个之前未声明的指向结构的指针,需要用到
- 记得使用
free(),尤其是删除节点时,否则会带来严重后果
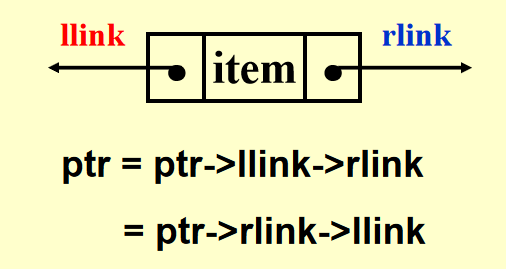
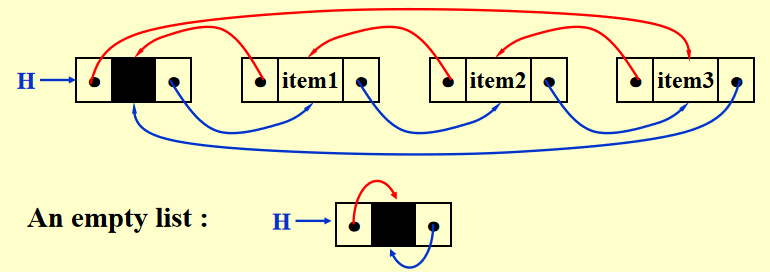
Double Linked Circular Lists⚓︎
图示:
声明:
typedef struct node *node_ptr;
typedef struct node
{
node_ptr llink;
element item;
note_ptr rlink;
};
例子:
作用:简化删除节点的过程
Applications⚓︎
The Polynomial ADT⚓︎
- Objects:\(P(x) = a_1x^{e_1} + \dots + a_nx^{e_n}\),有一组有序对 \(<e_i, a_i>\),其中 \(a_i\) 被称为系数 (coefficient);\(e_i\) 被称为指数 (exponent),为非负数
-
Operations:
Finding_degree:判断多项式的最高次AdditionSubtractionMultiplicationDifferentiation:求导
两种实现方法:
// 1. 数组——编写加法、乘法等函数较为简单,但会有很大的空间浪费
typedef struct
{
int CoeffArray[MaxDegree + 1];
int HighPower;
} *Polynomial;
// 2. 链表——节省空间,但编写加法、乘法和函数较为困难
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node
{
int Coefficient;
int Exponent;
PtrToNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToNode Polynomial; // 节点根据指数大小排序好
下面用数组形式编写加法和乘法函数
// Addition
void add_polynomial( POLYNOMIAL poly1, POLYNOMIAL poly2, POLYNOMIAL poly_sum )
{
int i;
zero_polynomial( poly_sum );
poly_sum->high_power = max( poly1->high_power, poly2->high_power);
for( i = poly_sum->high_power; i >= 0; i-- )
poly_sum->coeff_array[i] =
poly1->coeff_array[i] + poly2->coeff_array[i];
}
// Multiplication
void mult_polynomial( POLYNOMIAL poly1, POLYNOMIAL poly2, POLYNOMIAL poly_prod )
{
unsigned int i, j;
zero_polynomial( poly_prod );
poly_prod->high_power = poly1->high_power + poly2->high_power;
if( poly_prod->high_power > MAX_DEGREE )
error("Exceeded array size");
else
for( i = 0; i <= poly->high_power; i++ )
for( j = 0; j <= poly2->high_power; j++ )
poly_prod->coeff_array[i+j] +=
poly1->coeff_array[i] * poly2->coeff_array[j];
}
补充:链表实现加法函数(自己写的,有些啰嗦)
Polynomial Add( Polynomial a, Polynomial b )
{
PtrToNode head = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
head->Next = NULL;
Polynomial ans = head;
Polynomial cur = head;
while (a->Next != NULL && b->Next != NULL)
{
PtrToNode temp = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->Next = NULL;
if (a->Next->Exponent > b->Next->Exponent)
{
temp->Coefficient = a->Next->Coefficient;
temp->Exponent = a->Next->Exponent;
a = a->Next;
}
else if (a->Next->Exponent < b->Next->Exponent)
{
temp->Coefficient = b->Next->Coefficient;
temp->Exponent = b->Next->Exponent;
b = b->Next;
}
else
{
temp->Coefficient = a->Next->Coefficient + b->Next->Coefficient;
if (temp->Coefficient == 0)
{
a = a->Next;
b = b->Next;
free(temp);
continue;
}
else
{
temp->Exponent = a->Next->Exponent;
}
a = a->Next;
b = b->Next;
}
cur->Next = temp;
cur = cur->Next;
}
while (a->Next != NULL)
{
PtrToNode temp = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->Coefficient = a->Next->Coefficient;
temp->Exponent = a->Next->Exponent;
temp->Next = NULL;
cur->Next = temp;
a = a->Next;
cur = cur->Next;
}
while (b->Next != NULL)
{
PtrToNode temp = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->Coefficient = b->Next->Coefficient;
temp->Exponent = b->Next->Exponent;
temp->Next = NULL;
cur->Next = temp;
b = b->Next;
cur = cur->Next;
}
return head;
}
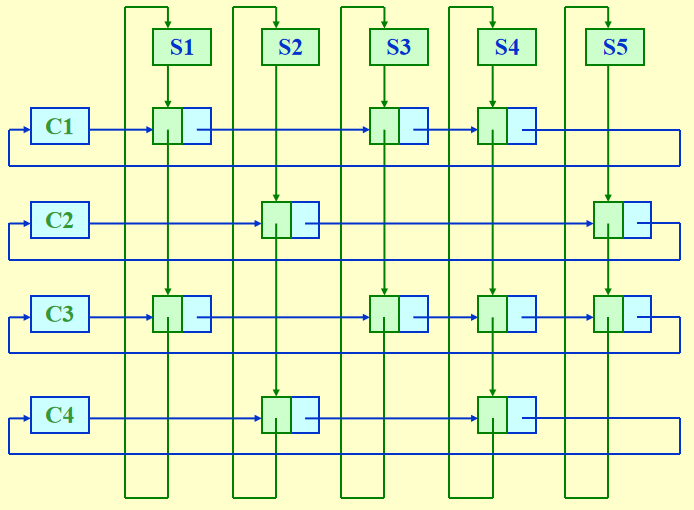
Multilists⚓︎
问题
有 40000 名学生和 2500 门课,要求列出每门课学生的名单,以及每位学生的课表
- 如果用数组(40000 \(\times\) 2500)做,会浪费巨大的空间。
- 因此用循环链表,而且对于链表的每个节点,有两组指针:
- 一组指向选这门课的其他学生
- 另一组指向这位学生的其他课程
图示:
然而,虽然看起来很优雅,但实现起来困难重重(想象一下插入和删除的操作
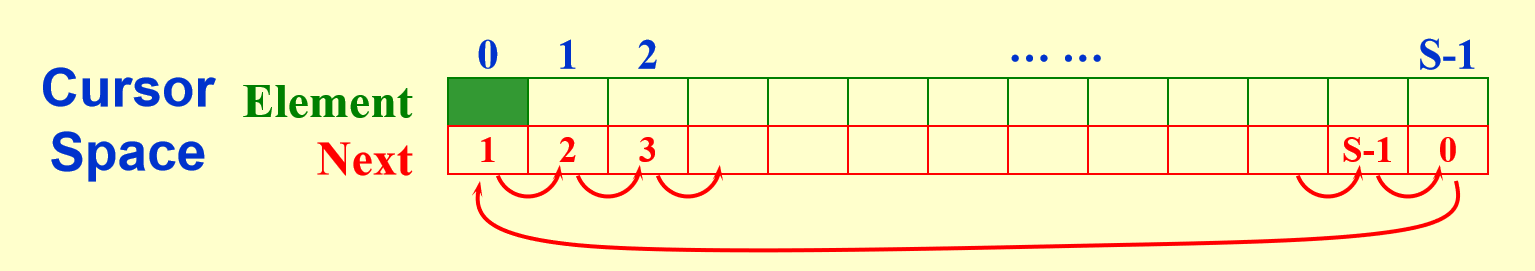
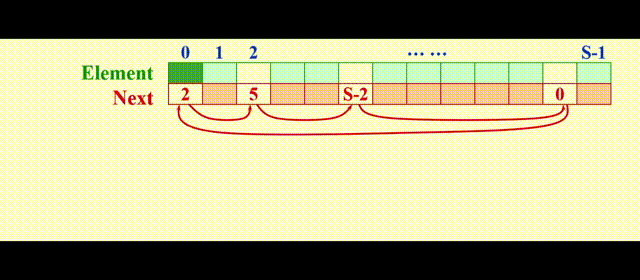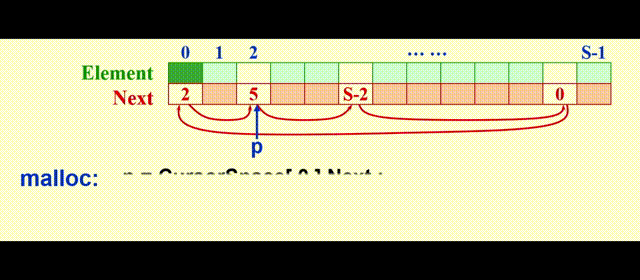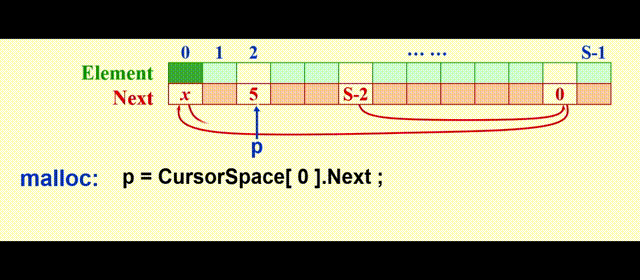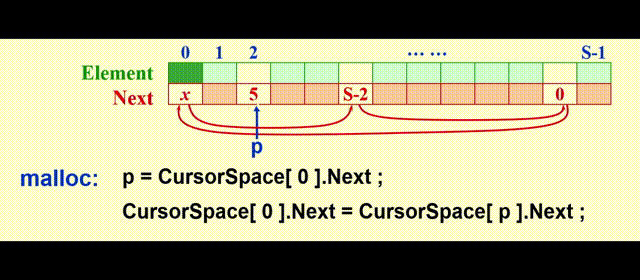
Cursor Implementation of Linked Lists⚓︎
用指针实现的链表的特征:
- 链表为一组结构体,每个结构体包含一个数据域和指针域(指向下一个结构)
- 通过
malloc()分配新的结构体,且通过调用free()释放
问题
对于一些没有指针类型的编程语言,如何做到不用指针实现链表呢?
——用游标实现 (cursor implementation)!
通常游标实现法比用指针更快,因为这种方法没有调用malloc()和free()等内存管理函数。我们可以用游标“模拟”基于指针的链表实现。
我们需要额外用一个列表 ( 被称为freelist ),保存不在原列表中的元素,模拟内存的空闲空间,这里我们用游标空间 (cursor space) 来实现,它的图示如下:
声明:
typedef unsigned int node_ptr;
struct node
{
element_type element;
node_ptr next;
};
typedef node_ptr LIST;
typedef node_ptr position;
struct node CURSOR_SPACE[SPACE_SIZE];
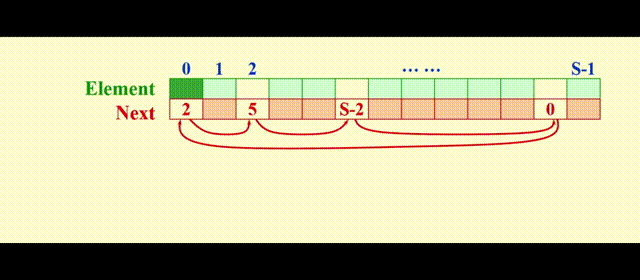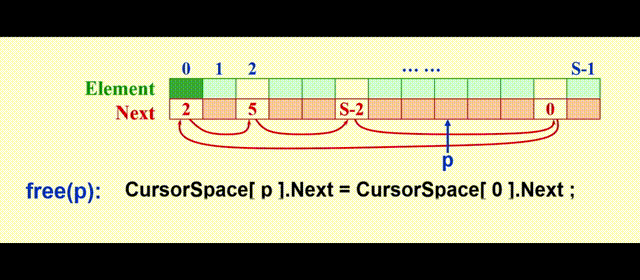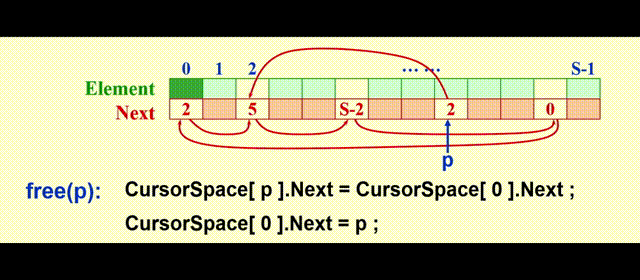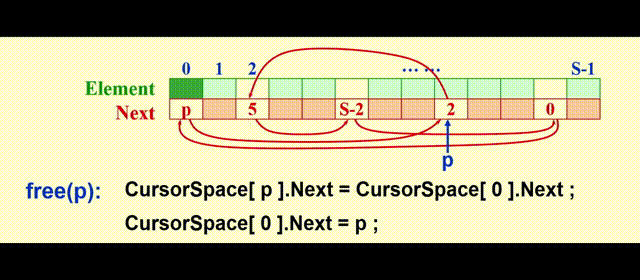
实现思路:
malloc:将表中第一个元素移出free:将新的位置放在表的前面
代码实现
// 链表的类型声明,一般放在.h文件中
#ifndef _Cursor_H
typedef int PtrToNode;
typedef PtrToNode List;
typedef PtrToNode Position;
void InitializeCursorSpace(void);
List MakeEmpty(List L);
int IsEmpty(List L);
int IsLast(Position P, const List L);
Position Find(ElementType X, const List L);
void Delete(ElementType X, List L);
Position FindPrevious(ElementType X, const List L);
void Insert(ElementType X, List L, Position P);
void DeleteList(List L);
Position Header(const List L);
Position First(const List L);
Position Advance(const Position P);
ElementType Retrieve(const Position P);
#endif
// 链表的具体实现,一般放在.c文件中
// 节点
struct Node
{
ElementType Element;
Position Next;
};
struct Node CursorSpace[SpaceSize];
// 假设游标分配和释放函数已有函数原型
// 游标分配
static Position CursorAlloc(void)
{
Position P;
P = CursorSpace[0].Next;
CursorSpace[0].Next = CursorSpace[P].Next;
return P;
}
// 游标释放
static void CursorFree(Position P)
{
CursorSpace[P].Next = CursorSpace[0].Next;
CursorSpace[0].Next = P;
}
// 检查链表是否为空
int IsEmpty(List L)
{
return CursorSpace[L].Next == 0;
}
// 检查节点 P 是否为最后一项
// 注意到链表 L 没有用上,放在这里以防特殊情况的处理
int IsLast(Position P, List L)
{
return CursorSpace[P].Next == 0;
}
// 查找数据 X 在链表 L 中的位置
Position Find(ElementType X, List L)
{
Position P;
P = CursorSpace[L].Next;
while (P && CursorSpace[P].Element != X)
P = CursorSpace[P].Next;
return P;
}
// 删除链表 L 中的数据 X
void Delete(ElementType X, List L)
{
Position P, TmpCell;
P = FindPrevious(X, L);
if (!IsLast(P, L))
{
TmpCell = CursorSpace[P].Next;
CursorSpace[P].Next = CursorSapce[TmpCell].Next;
CursorFree(TmpCell); // 删除节点时不要忘记释放内存!!!
}
}
// 在位置 P 后插入新数据 X
void Insert(ElementType X, List L, Position P)
{
Position TmpCell;
TmpCell = CursorAlloc();
if (TmpCell == 0)
FatalError("Out of Space!!!"); // 这里用到处理错误信息的自定义函数
CursorSpace[TmpCell].Element = X;
CursorSpace[TmpCell].Next = CursorSpace[P].Next;
CursorSpace[P].Next = TmpCell;
}
Supplement: Reverse a Linked List⚓︎
List Reverse( List L )
{
Position cur;
Position pre;
Position rear;
cur = L->Next;
while (cur != NULL)
{
rear = cur->Next;
if (cur == L->Next)
cur->Next = NULL;
else
cur->Next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = rear;
}
L->Next = pre;
return L;
}
The Stack ADT⚓︎
ADT⚓︎
stack( 栈 ):一种LIFO(last-in-first-out,后进先出 )的列表,即仅在有序列表的顶端 (top) 进行插入和删除操作
- Objects:拥有 0 个或多个元素的有限有序列表
- Operations:
Int IsEmpty(Stack S);:检查栈是否为空Stack CreateStack();:创建栈DisposeStack(Stack S);MakeEmpty(Stack S);:清空栈Push(ElementType X, Stack S);:插入新元素ElementType Top(Stack S);:获得栈顶元素Pop(Stack S);:删除栈顶元素
注意
- 对空的栈使用
Pop或Top操作将会引发栈 ADT 错误 - 对满的栈使用
Push操作将会引发实现错误 (implementation error)
Implementations⚓︎
Linked List Impletation⚓︎
代码实现
// .h文件代码:栈 ADT 的类型声明
#ifndef _Stack_h
struct Node;
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
typedef PtrToNode Stack;
int IsEmpty(Stack S);
Stack CreateStack(void);
void DisposeStack(Stack S);
void MakeEmpty(Stack S);
void Push(ElementType X, Stack S);
ElementType Top(Stack S);
void Pop(Stack S);
#endif /* _Stack_h*/
// .c 文件代码:链表方式的实现
struct Node
{
ElementType Element;
PtrToNode Next;
};
int IsEmpty(Stack S)
{
return S->next == NULL;
}
Stack CreateStack(void)
{
Stack S;
S = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (S == NULL)
FatalError("Out of space!!"); // 自定义函数
MakeEmpty(S);
return S;
}
void MakeEmpty(Stack S)
{
if (S == NULL)
Error("Must use CreateStack first"); // 自定义函数
else
while (!IsEmpty(S))
Pop(S);
}
void Push(ElementType X, Stack S)
{
PtrToNode TmpCell;
TmpCell = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (TmpCell == NULL)
FatalError("Out of space!!");
else
{
TmpCell->Element = X;
TmpCell->Next = S->Next;
S->Next = TmpCell;
}
}
ElementType Top(Stack S)
{
if (!IsEmpty(S))
return S->Next->Element;
Error("Empty stack");
return 0; // Return value used to avoid warning
}
void Pop(Stack S)
{
PtrToNode FirstCell;
if (IsEmpty(S))
Error("Empty stack");
else
{
FirstCell = S->Next;
S->Next = S->Next->Next;
free(FirstCell);
}
}
时间复杂度:常数 \(O(1)\)
缺点:多次使用 malloc() 和 free()开销太大
改进方法:额外创建一个栈,用于存放本来应该 free() 掉的空间,等到有新的元素需要 push 的时候就可以用这个“回收站”中的空间,而无需再使用 malloc()
Array Impletation⚓︎
代码实现
// .h 文件代码:栈 ADT 的类型声明
#ifndef _Stack_h
struct StackRecord;
typedef struct StackRecord *Stack;
int IsEmpty(Stack S);
int IsFull(Stack S);
Stack CreateStack(int MaxElements);
void DisposeStack(Stack S);
void MakeEmpty(Stack S);
void Push(ElementType X, Stack S);
ElementType Top(Stack S);
void Pop(Stack S);
ElementType TopAndTop(Stack S);
#endif /* _Stack_h*/
// .c 文件代码:(动态分配)数组方式的实现
#define EmptyTOS (-1) // 加括号是为了防止运算顺序的错误
#define MintackSize (5) // 同上
struct StackRecord
{
int Capacity;
int TopOfStack;
ElementType *Array;
};
Stack CreateStack(int MaxElements)
{
Stack S;
if (MaxElemets < MinStackSize)
Error("Stack size if too small");
S = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct StackRecord));
if (S == NULL)
FatalError("Out of space!!!");
S->Array = (ElementType *)malloc(sizeof(ElementType) * MaxElements);
if (S->Array == NULL)
FatalError("Out of Space!!!");
S->Capacity = MaxElements;
MakeEmpty(S);
return S;
}
void DisposeStack(Stack S)
{
if (S != NULL)
{
free(S->Array);
free(S);
}
}
int IsEmpty(Stack S)
{
return S->TopOfStack == EmptyTOS;
}
void MakeEmpty(Stack S)
{
S->TopOfStack = EmptyTOS;
}
void Push(ElementType X, Stack S)
{
if(IsFull(S))
Error("Full stack");
else
S->Array[++S->TopOfStack] = X;
}
ElementType Top(Stack S)
{
if (!IsEmpty(S))
return S->Array[S->TopOfStack];
Error("Empty stack");
return 0; // Return value used to avoid warning
}
void Pop(Stack S)
{
PtrToNode FirstCell;
if (IsEmpty(S))
Error("Empty stack");
else
{
S->TopOfStack--;
}
}
// 市面上很多教材都会把 Pop 和 Top 函数集成到 Pop 函数上
// 而本书的作者将两者分开,但他也提供了集成的版本(前面没有写函数原型)
ElementType TopAndPop(Stack S)
{
if(!IsEmpty(S))
return S->Array[S->TopOfStack--];
Error("Empty stack");
return 0; // Return value used to avoid warning
}
注
- 栈模型需要封装好。也就是说,除了栈相关函数外,代码的其他部分不能使用
Array或TopOfStack的变量 - 在执行
Push和Pop前必须进行错误检查
Applications⚓︎
Balancing Symbols⚓︎

伪代码实现:
Algorithm
{
Make an Empty stack S;
while (read in a character c)
{
if (c in an opening symbol)
Push(c, S);
else if (c is a closing symbol)
{
if (S is empty)
{
ERROR;
exit;
}
else // stack is okay
{
if (Top(S) does not match c)
{
ERROR;
exit;
}
else
Pop(S);
} // end else-stack is okay
} // end else-if-closing symbol
} // end while-loop
if (S is not empty)
ERROR;
}
时间复杂度:\(O(N)\),这是一个在线算法
Postfix Evaluation⚓︎
处理步骤:
- 遇到操作数,将其压入栈中
- 遇到运算符 \(opt\),弹出栈最顶上两个元素 \(a, b\),其中 \(top = a\),然后计算 \(c = b\ opt\ a\),最后将 \(c\) 压入栈中
- 遍历完后缀表达式后,栈中应当剩下一个元素,该元素即为最终结果
注:后面讲到的表达式树的构建也采用类似步骤
代码实现
// 这里的栈用的是数组表示法
// 而且该算法只能处理 10 以内的整数四则运算,仅供参考
int PostExp(char * exp, stack S)
{
int len;
int i;
element a, b;
int ans;
len = strlen(exp);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (exp[i] == ' ' || exp[i] == '\n')
continue;
else if (isdigit(exp[i]))
Push(exp[i], S);
else
{
b = Pop(S);
a = Pop(S);
if (!a || !b)
{
printf("wrong expression!\n");
return INT_MAX; // 无穷大表示错误信号
}
switch(exp[i])
{
case '+':
Push(a + b - '0', S);
break;
case '-':
Push(a - b + '0', S);
break;
case '*':
Push((a - '0') * (b - '0') + '0', S);
break;
case '/':
Push((a - '0') / (b - '0') + '0', S);
break;
default:
printf("wrong expression!\n");
return INT_MAX;
}
}
}
ans = Pop(S) - '0';
return ans;
}
Infix to Postfix Conversion⚓︎
关键点
- 操作数 (operands)的顺序不变,因此直接输出
- 在栈内,高优先级的运算符 (operators)在低优先级运算符的前面
- 注意:如果‘(’不在栈内,则它的优先级最高;如果它在栈内,则优先级最低
具体实现
- 如果待判断的运算符的优先级高于栈顶运算符 ( 包括
(),或者栈内无元素,将其压入栈 - 否则,若运算符是
),则将栈内包括(前的所有运算符按出栈顺序弹出((也仅在该情况下才能弹出) - 否则的话,从栈顶开始依次弹出运算符,直到满足条件 1,再将该运算符压入栈中
注:上述原则适用于加减乘除四则运算,但不适合幂运算,因为幂运算符 ^ 结合方向自右向左
代码实现
// 直接摘自我的 project 2
Queue InToPost(char * exp)
{
char * tmp = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * VLENGTH); // Containing the variables or constant
Stack s; // The stack for operators, in order to getting the proper order in postfix form
Queue q; // The postfix expression, split them into variables, constants and operators in a queue
char opt; // The operator
char * head = exp; // Cheking if it's the first character in the expression
// Initialization
s = CreateStack();
q = CreateQueue();
tmp[0] = '\0';
while (*exp != '\0') // Traversing the infix expression
{
if (isalnum(*exp)) // Finding the potential variables and constants
{
CharToString(*exp, tmp); // Receiving it
}
else if (*exp == '-' && (exp == head || *(exp - 1) == '(')) // Handling with the case with minus sign
{
Enqueue("0", q);
Push2(*exp, s);
}
else // If it's an operator
{
if (strlen(tmp)) // If there is a variable or a constant
{
if (*exp == '(' && (!strcmp(tmp, "sin") || !strcmp(tmp, "cos") || !strcmp(tmp, "ln"))) // Dealing with math functions
{
Enqueue("0", q);
switch (tmp[0])
{
case 's': // sin
Push2('!', s);
break;
case 'c': // cos
Push2('@', s);
break;
case 'l': // ln
Push2('#', s);
break;
}
}
else
Enqueue(tmp, q); // Outputting it
tmp[0] = '\0'; // Resetting
}
// If it's an empty stack or the priority of the current operator is higher than the top element, or the top element is the left parentheses
if (IsEmpty(s) || priority(*exp) < priority(s->top->operator) || s->top->operator == '(')
Push2(*exp, s); // Pushing the operator into the stack
else if (*exp == ')') // If it's a right parentheses
{
while (s->top->operator != '(') // Poping out all the operators on the left parentheses in the stack
{
opt = Top2(s);
Pop(s);
CharToString(opt, tmp);
Enqueue(tmp, q); // Don't forget to output it!
tmp[0] = '\0'; // Resetting
}
Pop(s); // Don't forget throw the left parentheses out!
while (s->top->operator == '!' || s->top->operator == '@' || s->top->operator == '#') // Coping with math functions, but unluckily, there are still some bugs
{
opt = Top2(s);
Pop(s);
CharToString(opt, tmp);
Enqueue(tmp, q); // Don't forget to output it!
tmp[0] = '\0'; // Resetting
}
}
else // Else Poping out all elements with the higher priority out, until encountering the '(' or the lower one
{
while (s->top->operator != '(' && priority(*exp) >= priority(s->top->operator))
{
opt = Top2(s);
Pop(s);
CharToString(opt, tmp);
Enqueue(tmp, q); // Don't forget to output it!
tmp[0] = '\0'; // Resetting
}
Push2(*exp, s); // Pushing the new one to the stack
}
}
exp++; // Checking the next one
}
// Dealing with the remaining part(important!)
if (strlen(tmp))
{
Enqueue(tmp, q);
tmp[0] = '\0';
}
while (!IsEmpty(s)) // Disposing of the remaining elements in the stack
{
if (Top2(s) != '(' && Top2(s) != ')') // Special case for parentheses
{
opt = Top2(s);
Pop(s);
CharToString(opt, tmp);
Enqueue(tmp, q);
tmp[0] = '\0';
}
else
Pop(s);
}
return q; // Returing the output sequence
}
注:
- 这里的代码是针对 project 的问题“定制”的,因此可能不太具有通用性
- 这里我将得到的后缀表达式存储为队列,是为了方便后续构建表达式树
Function Calls⚓︎
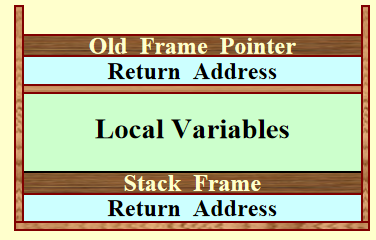
每一次函数调用产生的数据,包括局部变量 (local variables) 和返回地址 (return address),都会被存入到栈帧 (stack frame)当中,而这个帧会被存到系统栈 (system stack)中。
由于系统不会检查栈溢出 (overflow)的情况,因此当调用函数过多时会带来灾难性后果(比如漏掉基本情况的递归函数)
尾部递归 (tail recursion):递归函数在最后一行进行递归调用。这时系统往往将递归函数改写成循环形式(goto,当然自己写循环时千万别用这个
// Recursion
void PrintList(List L)
{
if (L != NULL)
{
PrintElement(L->Element);
PrintList(L->Next);
}
} // a bad use of recursion
// Iteration
void PrintList(List L)
{
top: if (L != NULL)
{
PrintElement(L->Element);
L = L->Next;
goto top;
} // do NOT do this!
} // compiler removes recursion
The Queue ADT⚓︎
ADT⚓︎
队列 (queue):一种FIFO(first-in-first-out,先进先出 )的列表,即在有序列表的一端插入,另一端删除
- Objects:拥有 0 个或多个元素的有限有序列表
-
Operations:
Int IsEmpty(Queue Q);:检查队列是否为空Stack CreateQueue();:创建队列DisposeQueue(Queue Q);MakeEmpty(Queue Q);:清空队列Enqueue(ElementType X, Queue Q);:入队ElementType Front(Queue Q);:获得队首元素Dequeue(Queue Q);:出队
Array Implementation⚓︎
代码实现
// .h文件代码:队列ADT的类型声明
#ifndef _Queue_h
struct QueueRecord;
typedef struct QueueRecord *Queue;
int IsEmpty(Queue Q);
int IsFull(Queue Q);
Stack CreateQueue(int MaxElements);
void DisposeQueue(Queue Q);
void MakeEmpty(Queue Q);
void Enqueue(ElementType X, Queue Q);
ElementType Front(Queue Q);
void Dequeue(Queue Q);
ElementType FrontAndDequeue(Queue Q);
#endif /* _Queue_h*/
// .c 文件代码:(动态分配)数组方式的实现
#define MintackSize (5) // 加括号是为了防止运算顺序的错误
struct QueueRecord
{
int Capacity;
int Front;
int Rear;
int Size;
ElementType *Array;
};
int IsEmpty(Queue Q)
{
return Q->Size == 0;
}
void MakeEmpty(Queue Q)
{
Q->Size = 0;
Q->Front = 1;
Q->Rear = 0;
}
// 形成循环队列
static int Succ(int Value, Queue Q)
{
if (++Value == Q->Capacity)
Value = 0;
return Value;
}
void Enqueue(ElementType X, Queue Q)
{
if (IsFull(Q))
Error("Full Queue");
else
{
Q->Size++;
Q->Rear = Succ(Q->Rear, Q);
Q->Array[Q->Rear] = X;
}
}
void Dequeue(Queue Q)
{
if (IsEmpty(Q))
Error("Empty Queue");
else
{
Q->Size--;
Q->Front = Succ(Q->Front, Q);
}
}
ElementType Front(Queue Q)
{
if (IsEmpty(Q))
Error("Empty Queue");
else
return Q->Array[Q->Front];
}
上述代码中采用了循环队列 (circular queue)的方法,能够最大化利用队列的空间。对于循环队列,区分空队列和满队列有 2 种做法:
- 空出一块空间
- 增加一个
Size的字段,用来实时统计队列元素个数,这样无需浪费空间(上述代码便采用这种做法)在法 2 中,如果用
front表示队首元素,size表示当前队伍大小,m表示队伍最大大小,则队尾元素rear = (front + size - 1) % m
Linked List Implementation⚓︎
代码实现(直接摘自我的某个作业)
// Declaration
typedef struct QueueNode * PtrToQueue; // The pointer to a queue node
typedef struct queue * Queue; // The actual queue
struct QueueNode // The node(double linked list)
{
char var[VLENGTH];
PtrToQueue next; // The pointer to the next node
PtrToQueue pre; // The pointer to the previous node
};
struct queue // just a structure, the real one is defined above!
{
PtrToQueue front;
PtrToQueue rear;
int size;
};
int IsEmptyQ(Queue Q); // Detecting whether the queue is empty
Queue CreateQueue(); // Creating the queue
void DisposeQueue(Queue Q); // Clearing the queue
void Enqueue(char * x, Queue Q); // Putting the element into the queue
char * Front(Queue Q); // Obtaining the front element
void Dequeue(Queue Q); // Deleting the front element
// Functions
int IsEmptyQ(Queue Q)
{
return Q->size == 0; // Just Cheking the size
}
// Creating the queue
Queue CreateQueue()
{
Queue q;
// Allocating spaces for the while queue, the front node and the rear node
q = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(struct queue));
q->front = (PtrToQueue)malloc(sizeof(struct QueueNode));
q->rear = (PtrToQueue)malloc(sizeof(struct QueueNode));
q->front = q->rear; // Letting the front pointer and the rear pointer point to the same position, representing the empty queue
q->size = 0; // Letting the size be 0(empty)
return q;
}
// Clearing the queue
void DisposeQueue(Queue Q)
{
while (!IsEmptyQ(Q)) // Deleting all the element until all the element is out
Dequeue(Q);
}
// Putting the element into the queue
void Enqueue(char * x, Queue Q)
{ // Allocating a space for the temporary node
PtrToQueue tmp = (PtrToQueue)malloc(sizeof(struct QueueNode));
strcpy(tmp->var, x); // Assignment
tmp->pre = Q->rear; // Building the relationship with the originally rear node
tmp->next = Q->rear->next;
Q->rear->next = tmp;
Q->rear = tmp; // Setting the new node as the rear node
Q->size++; // Incrementing the size
}
// Obtaining the front element
char * Front(Queue Q)
{
if (!IsEmptyQ(Q)) // If not empty, obtaining the front node
return Q->front->next->var;
printf("Empty Queue!!!\n"); // Warning!!!
return 0;
}
// Deleting the front element
void Dequeue(Queue Q)
{// Allocating a space for the temporary node
if (IsEmptyQ(Q)) // Warning!
printf("Empty Queue!!!");
else
{
PtrToQueue tmp = Q->front->next; // Remember the queue has a dummy header!
Q->front->next = tmp->next; // Setting the next node as the new front node
tmp->next->pre = Q->front;
free(tmp); // Deleting the originally front node
Q->size--; // Decrementing the size
}
}
Applications⚓︎
- 操作系统中的任务安排:每个任务按照 FIFO 原则执行
这里有个小问题:每个任务可以在中途
kill掉,这不符合队列的出队方法
评论区